
Menu
Circular Innovation Council has been commissioned by Canadian Standards Association (CSA) Group to undertake research on the current landscape on repairability, and provide guidance on potential development of standard(s) that would support advanced repairability options and access across Canada. This exercise will also identify sector-specific issues, as well as market and policy levers, that are necessary to advance repairability access and acceptance.

Circular Innovation Council is conducting interviews with key stakeholders who can support and contextualize supporting research around technical, market, policy and legal conditions. We have also convened an Advisory Panel of individuals who have specific expertise and experience advancing repairability in Canada an
Circular Innovation Council is developing a report that summarizes the findings of the landscape research and stakeholder interviews. These findings will define and quantify, where possible, how reparability will be critical for advancing circular economies in Canada; and provide deeper insights into how a broader standard can support improved transparency, consumer protections, and competitive fairness.
By extending the useful lifespan and value of products and materials inherent to them, repair and reuse are core components for advancing a circular economy in Canada. Specific sectors will rely heavily on comprehensive, innovative right to repair standards in order to achieve circular outcomes for their products or services.
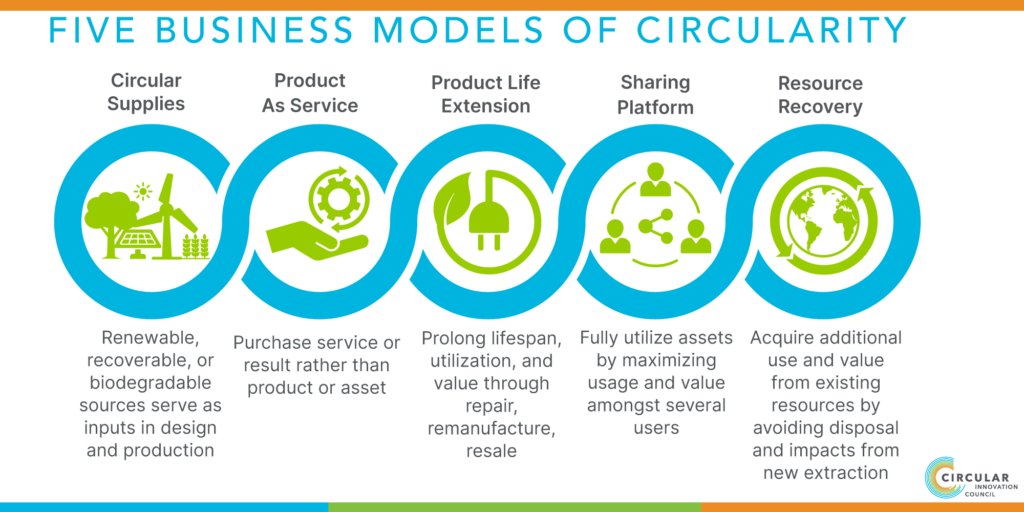
Designing for circularity also necessitates that produces have reparability, durability, and reuse as key considerations at the design stage. Conversely, without the ability for Canadian consumers to access instructions, tools and components necessary to facilitate repair and reuse in or to extend the life of products, other core tenets of circular economies will fall short in achieving desired outcomes.
In the absence of right to repair options, many durable goods sectors, including the Information Technology sector, appliances, automobiles, and agriculture will continue to encounter and encourage shortened lifespans, disposability, and planned obsolescence.
Currently the tools and software to fix digital devices and machinery are often closely guarded by manufacturers and right to repair is considered an infringement on intellectual property rights.
Circular Innovation Council is a registered charity.
Charity Registration Number: 119112118 RR 0001